For years, Google has captured about 90% of the search engine market share–generative engine optimization is changing that. Google processes nearly 8.5 billion searches every day, so it’s no wonder marketers want to rank at the top of Google SERPs.
But with the advent of generative search, that’s now changing.
While Google still dominates search, people are using the likes of ChatGPT and Gemini more and more to conduct online searches. To make sure your brand appears when people are using these chatbots, you need to optimize your website and content for AI search.
Read on to learn about generative engine optimization (GEO) to make sure your brand appears when people are searching for the types of products and services you are offering.
What Is Generative Engine Optimization?
Generative engine optimization (GEO) refers to optimizing your content so that generative AI tools, like ChatGPT’s SearchGPT, can find it.
Generative AI tools often act like search engines.
People seek answers from ChatGPT, Gemini, and similar platforms. These tools synthesize information from the web and often cite sources where they found the information.
Optimizing for generative search engines helps your brand appear in these results. When generative tools use you as a source, you benefit from brand mentions, links to your site, and free traffic that will increase your exposure.
How Does Generative Engine Optimization Work?
GEO relies on aligning your content with what people are searching for on generative AI platforms and how they’re searching for it.
Searches on tools like ChatGPT take a slightly different approach than a standard Google search.
Instead of just using keywords, people are typing long, highly specific queries into gen AI tools. They’re using natural language that sounds conversational, so GEO is more focused on search intent rather than keywords and metadata.
For example, let’s say you want to know the best annuities to invest in today. Here’s what we get when we asked ChatGPT:

Notice the source links?
Those are direct recommendations from ChatGPT, and users can click those links to learn more about each option.
In this case, GEO relies on a few factors:
- Timely content (the prompt requested information from today)
- Search intent (the prompt indicates a readiness to buy)
- Keywords (each result contains the word “annuity”)
- Accurate descriptions (each result clearly displays the name of the annuity, the rate, and a brief description)
- Context (asking follow-up questions in the same thread leads to more refined results)
The goal of GEO is to create content that most closely aligns with what a generative engine will create.
That means providing succinct yet thorough answers and information that’s easy to understand and matches what people are searching for.
Traditional SEO vs. GEO: Similarities & Differences
Now, let’s look at how traditional SEO and GEO compare.
| SEO | GEO | |
| Main Purpose | Relies heavily on keywords and metadata (and also search intent) | Aims to understand the user’s search intent |
| Where It Applies | Traditional search engines like Google and Bing | Generative AI tools like Gemini, ChatGPT, and Google’s AI Overviews |
| Ranking Factors | Results are ranked according to 200+ factors, including site age, quality signals, and domain authority | Fewer results displayed and doesn’t use a ranking system |
| Success Metrics | Click-through rates, bounce rates, time on page, etc. | Impressions to determine the number of appearances in gen AI results |
| Establishing Credibility and Authority | Backlinks, keywords, traffic, dwell time | Quality citations, statistics, and recent news |
| Optimization Strategies | Applies similar strategies to a broad range of content types (e.g., blog posts, videos, web pages) | Uses unique strategies based on content type and topic |
| How to Capture User Attention | Headlines and meta descriptions, where users click the result to learn more | Clear descriptions or explanations related to the query, often answering a query without the user having to click through |
There’s quite a bit of overlap between SEO and GEO.
First and foremost, both rely on quality content that addresses the user’s query. But SEO and GEO go about responding to queries in different ways.
Traditional SEO places some of the control in the searcher’s hands when it comes to rankings. Users see a page of possible results and can decide which one to click. Things like headlines, meta descriptions, and brand recognition play a role in this process.
GEO is more nuanced.
Users aren’t overwhelmed with options; instead, generative engines cherry-pick a few of the most relevant sources to share. It also tailors its response to each query, so even users who search for similar terms but phrased a little differently will have two totally different experiences.
Let’s look at how this works. We’ll use “Describe some of the best essential oils for sleep” and “What are three of the best essential oils for sleep?” as our queries to compare.
Here’s what ChatGPT returned for the first query:
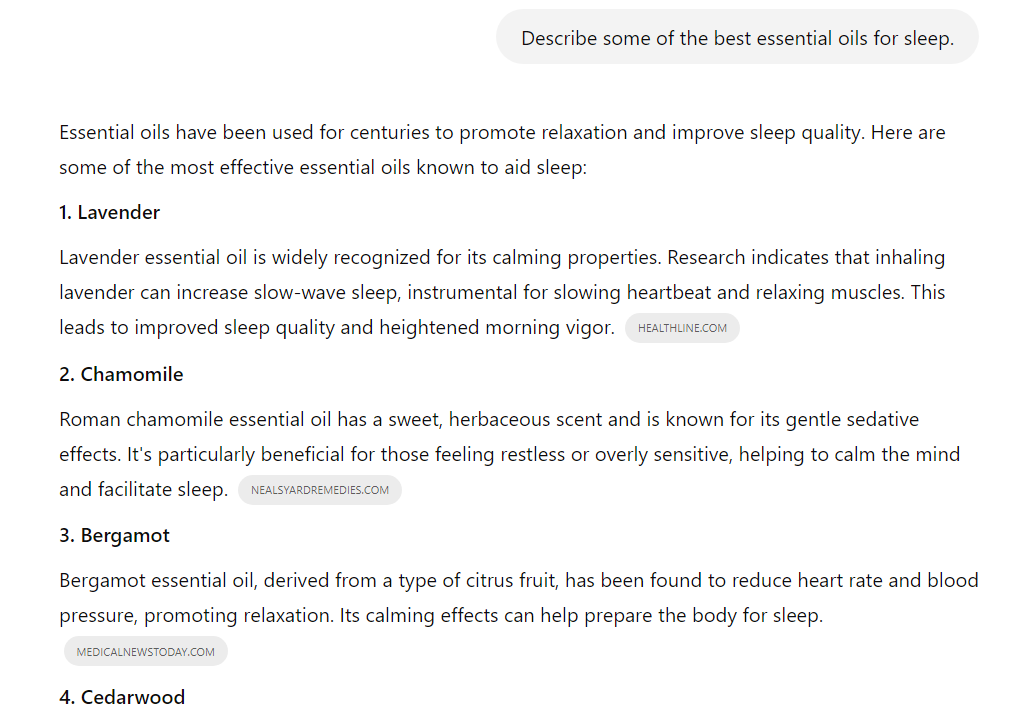
This image is clipped — there were several more results below the fourth point.
Now let’s compare to the second query, also made in ChatGPT:

Two similar searches, two very different results.
Each response lists different websites as sources, even though the topic was the same. Generative search engines thrive on custom results for each searcher based on how they phrase their query.
If you’ve been in SEO for any length of time, you know it’s a data-driven game. There’s no shortage of tools to help you find keywords and their monthly search volume and difficulty rating (think UberSuggest, Ahrefs, etc.).
There are also tools out there that will help you optimize your website for search engines. For example, website auditing tools like SEOptimer focus on technical improvements that search engines take into account.
The same can’t be said for generative engine results, at least not yet. We’re still largely in the dark about what people are searching for on ChatGPT, Gemini, and similar tools.
And even if we had access to it, sorting through and using it would look vastly different than, say, doing basic keyword research. Remember, every prompt is unique and results are custom to the user.
GEO Strategies: How to Rank in AI Search
Even though there isn’t GEO-specific data available yet, you can implement several strategies to increase the chances of your content appearing in generative AI search results. Here’s how you can optimize your content for AI-driven search engines:
Use SEO As a Foundation
GEO is built on SEO, so don’t give up on your SEO strategies just yet. SEO data is still the best resource for figuring out what people want to know, even if they’re using generative AI engines to search for answers.
The more you rank in traditional search, the better chance you have of being picked up by GEO engines.
That said, try to include more specific searches in your content. For example, you can use long-tail keywords or create timely content that provides info about the here and now.
Ensure Technical SEO is AI-Friendly
Even though GEO shifts focus from traditional SEO, technical factors still matter. Ensure:
- Your site loads quickly and is mobile-optimized.
- Content is structured using proper HTML headings, schema markup, and metadata.
- URLs are clean, readable, and well-organized.
Optimize for Conversational Queries
Generative AI search tools prioritize natural language queries. Instead of short-tail keywords, focus on long-tail, conversational phrases that match how users ask questions.
AI tools like ChatGPT and Gemini process full-sentence searches rather than just keywords. Your content should mirror this style by answering questions in a direct, engaging, and natural way.
For example, instead of structuring content around “best Bitcoin wallets,” phrase it as “What are the best Bitcoin wallets for security and ease of use?” This aligns with how users interact with generative AI platforms.
Provide Direct, Comprehensive Answers
Unlike traditional search engines that encourage users to click through multiple links, generative AI models aim to deliver the most useful response immediately.
Your content should provide clear, well-structured answers that generative AI can easily summarize and use as a citation.
- Structure content in a way that AI can easily parse (e.g., Q&A format, bullet points, numbered lists).
- Offer succinct, accurate, and detailed answers that fully address the user’s query.
- Include up-to-date, factual information backed by reputable sources.
Build a Strong Brand Presence Across the Web
AI tools don’t just pull from a single source; they evaluate a brand’s overall authority and credibility. This means your digital presence must extend beyond your website. Make sure you:
- Publishing authoritative content on multiple platforms (guest blogs, LinkedIn articles, etc.).
- Building backlinks from reputable sources to boost your domain authority.
- Increasing brand mentions across the web by engaging in industry discussions, forums, and social media.
Focus on Topical Authority
Generative AI values sources that demonstrate expertise and authority on a subject. Cover topics in depth on your blog, creating interconnected content hubs that explore subtopics extensively.
For example, if your website covers Bitcoin security, don’t just write a single article—develop a series covering private key management, cold storage, hardware wallets, and multisig setups.
AI search engines are more likely to cite a site recognized for its depth of knowledge in a specific domain.
Include Source Citations & Fresh Data
AI tools favor content that references current data and reputable sources.
To enhance your visibility:
- Regularly update content with the latest stats, research, and expert insights.
- Cite authoritative sources like studies, reports, and industry leaders.
- Use structured data (schema markup) to help AI understand the context of your content better.
Experiment with Short-Form & Easily Digestible Content
While long-form content is still valuable, AI search tools often extract shorter snippets of information.
Create concise, informative sections within your content to maximize AI discoverability:
- Write clear, direct answers to common questions within the first few sentences of a section.
- Use bullet points and tables to break down complex information.
- Create standalone Q&A content that AI can easily process.
Leverage Multimedia Content
Generative AI engines may reference multiple content formats, including images, infographics, and videos. Enhancing your content with rich media can improve visibility. Consider:
- Embedding short video explanations.
- Using diagrams or step-by-step visual guides.
- Creating AI-friendly transcripts for videos and podcasts.
Monitor AI Mentions & Adapt
Since AI search doesn’t provide keyword tracking tools like traditional SEO (yet), monitor where your content is appearing by:
- Running AI-generated searches for your brand name and key topics.
- Tracking referral traffic from AI-generated search links.
- Analyzing search trends and adapting your content accordingly.
Generative AI search is reshaping digital discovery, requiring brands to rethink their approach to search visibility.
How is GEO Changing the Search Marketing Landscape?
Generative AI search engines like ChatGPT and Gemini offer a distinct new look and feel, especially from a search marketing standpoint. If you’ve used these platforms yourself, you might notice:
- There are zero ads
- Results are limited and not ranked
- Results often cite multiple sources (and in some cases, no sources)
It’s a whole new search experience compared to traditional Google or Bing searches, and its simplicity is arguably its greatest advantage.
People aren’t shy about using these new search tools, either. ChatGPT alone has 300 million weekly users and processes more than a billion queries each day.
While traditional search engines focus on things like backlinks, clicks, and time on page to determine content quality, generative engines focus more on semantic relevance–the content that best matches the query.
That’s not to say that factors like backlinks and clicks don’t matter. They still do!
But ChatGPT doesn’t continue to suggest a result based on how many people click on that result, unlike Google. Instead, the focus is on how well the content matches the user’s search query.
With no pay-to-win options and a whole different way to measure quality results, marketers need to rely on the content itself to do the job.
This means creating topical authority, clearly and completely addressing the topic, and providing helpful, accurate claims that you can back up with sources.
Need Help with GEO? Talk to Us!
Web3 brands should start adapting now to keep their content visible and relevant, especially as more people start using generative AI engines to unlock answers to their most pressing questions.
Curious to see what GEO looks like in action? Reach out to us to help you rank in AI search.
FAQs
What’s the difference between SEO and GEO?
Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to optimizing website content for traditional search engines like Google and Bing. Generative engine optimization (GEO) refers to optimizing content for generative AI platforms like Gemini, ChatGPT, and Google’s AI Overviews.
Is GEO replacing SEO?
GEO is not replacing SEO. People still use Google and other search engines, so SEO still has an important place in marketing. GEO gives your audience another way to find and engage with you.
How to optimize for generative AI?
You can optimize your content for generative AI by fully and succinctly answering user queries, citing sources and recent stats, using conversational language, and making your content easy to read.
What is generative AI in SEO?
Many search engines like Google are including generative AI search results. Generative AI provides a brief summary or response to a query, offering a quick answer without having to click through multiple links or results.
How does generative AI affect SEO?
Generative AI gives web searchers an alternative to traditional search engines. SEO will be an essential element of generative AI as it helps gen AI platforms identify relevant content for users’ queries.




